When implementing a business automation guide strategy, organizations discover transformative opportunities to streamline workflows and eliminate time-consuming tasks that drain resources and limit growth potential.
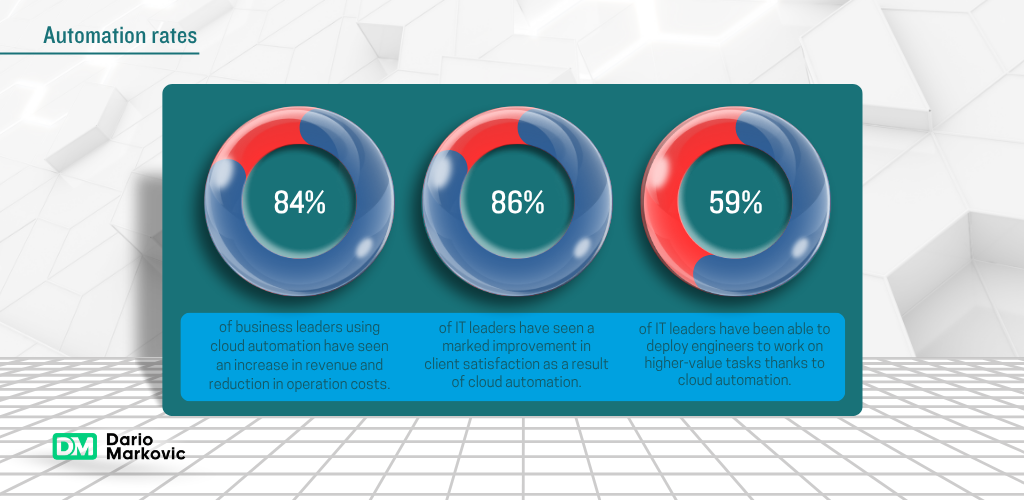
The landscape of business operations has fundamentally shifted. According to McKinsey & Company, businesses that embrace automation technologies can increase productivity by up to 40% while significantly reducing operational costs. Yet many business leaders struggle to identify where to begin their automation journey.
This ultimate guide provides a step-by-step framework for automating business processes across your organization, from simple repetitive tasks to complex processes requiring artificial intelligence and robotic process automation.
What is Business Automation? Understanding the Fundamentals
Business automation represents the strategic use of technology to perform routine tasks and business functions with minimal human intervention. By implementing automated systems, organizations replace manual processes with automated workflows that execute consistently, accurately, and efficiently.
Types of Business Automation
Modern business automation encompasses several categories:
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Software robots that mimic human behavior to complete manual tasks like data entry, invoice processing, and report generation. According to Gartner, RPA can reduce processing time by 80% for routine administrative tasks.
AI-Powered Automation: Advanced systems leveraging artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing to handle complex tasks requiring decision-making capabilities and real-time analysis.
Business Process Management (BPM): Comprehensive automation platforms that orchestrate end-to-end automation across multiple business functions, ensuring seamless workflow integration.
Marketing Automation: Tools that automate marketing activities like email marketing campaigns, lead generation, and customer relationship management to enhance customer experience.
Sales Automation: Systems that streamline operations for sales teams, automating follow-ups, pipeline management, and customer communications.
Key Benefits of E-Commerce Automation
The benefits of automation extend across every aspect of business operations:
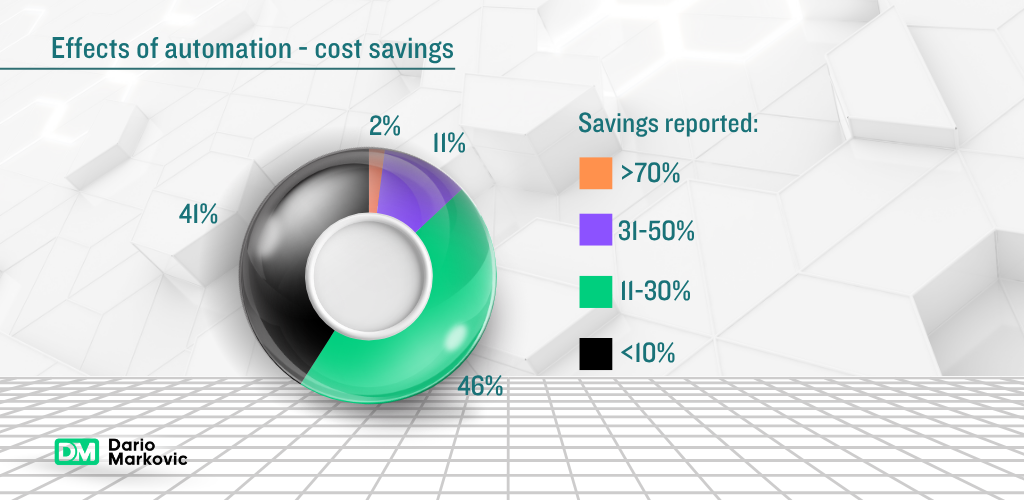
- Cost Reduction: Decrease labor costs and operational costs by up to 60% through automation processes
- Enhanced Accuracy: Eliminate human error in data processing and manual labor
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Deliver faster customer support and superior customer experience through real-time responses
- Operational Efficiency: Free up valuable time for team members to focus on strategic initiatives requiring critical thinking
- Scalability: Enable business growth without proportional increases in workforce or resources
- Better Decision-Making: Access predictive analytics and real-time data for informed business strategy
Why Business Automation Matters in 2026?
The power of AI and automation technologies has reached unprecedented levels.
Deloitte research indicates that 73% of organizations have already begun implementing automation initiatives, with digital transformation accelerating across businesses of all sizes.
The Competitive Imperative
Organizations that delay automation adoption face significant competitive disadvantages:
- Increased Labor Costs: Manual processes become increasingly expensive as talent costs rise
- Slower Response Times: Manual workflows cannot match the speed of automated systems
- Limited Scalability: Growth requires linear increases in headcount without automation
- Data Disadvantage: Competitors using automation gain superior insights through advanced analytics
Emerging Automation Technologies
Several game-changer technologies are reshaping business automation:
AI Agents: Autonomous systems capable of handling complex processes across multiple business tasks without human intervention
Process Mining: Advanced analytics that identify automation opportunities by analyzing existing workflows and bottlenecks
Intelligent Document Management: AI-powered systems that process, categorize, and extract insights from unstructured data
Predictive Analytics: Machine learning models that forecast trends, optimize inventory management, and anticipate customer needs
The Complete Guide: 5-Step Business Automation Framework

Step 1: Identify Automation Opportunities Through Process Analysis
Successful automation implementation begins with comprehensive process improvement analysis. Business owners and business leaders must conduct thorough audits to pinpoint where automation delivers maximum impact.
Conducting Your Automation Audit
Map Current Workflows: Document all business processes step-by-step, identifying:
- Time-consuming tasks consuming excessive resources
- Repetitive tasks performed daily or weekly
- Manual effort prone to human error
- Bottlenecks limiting operational efficiency
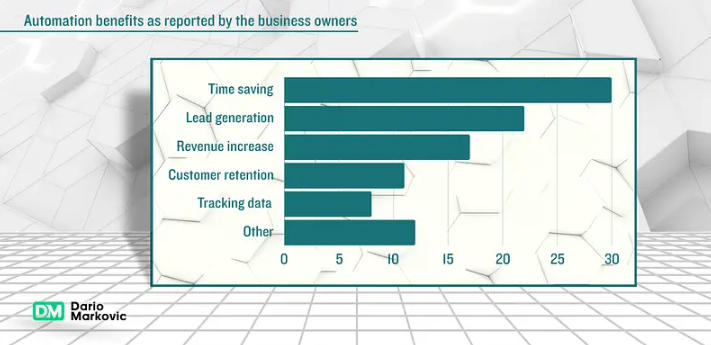
Analyze Resource Allocation: Examine where team members spend valuable time. Harvard Business Review research shows that knowledge workers spend 41% of their time on routine tasks that could be automated.
Prioritize Based on Impact: Use this framework for automation workflows:
- High Impact + Easy Implementation: Quick wins like email automation, automated responses, and basic data entry
- High Impact + Complex Implementation: Strategic priorities such as supply chain management and accounts payable automation
- Low Impact + Easy Implementation: Secondary opportunities worth pursuing with available resources
- Low Impact + Complex Implementation: Deprioritize unless aligned with long-term business strategy
Common Processes Ripe for Automation
Employee Onboarding: Automate the onboarding process for new employees, including document management, training scheduling, and system access provisioning
Customer Support: Implement chatbots and automated ticketing systems to handle routine inquiries 24/7
Financial Services: Streamline operations for invoice processing, expense approvals, and accounts payable workflows
HR Processes: Automate leave requests, performance review scheduling, and benefits administration
Inventory Management: Deploy automated systems for stock tracking, reordering, and warehouse management
Marketing Activities: Automate email marketing, social media scheduling, and lead generation campaigns
Step 2: Define Clear Business Objectives and Success Metrics
Business automation software and automation tools only deliver value when aligned with specific business needs and measurable goals.
Setting SMART Automation Goals
Establish objectives that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound:
- Reduce invoice processing time from 5 days to 24 hours within 3 months
- Decrease customer support response time by 70% through automated workflows
- Cut operational costs by 35% in the first year of automation implementation
- Improve customer satisfaction scores by 25% through enhanced user experience
- Eliminate 90% of manual data entry errors within 6 months
Aligning Automation with Business Growth
Your automation strategy should support broader organizational objectives:
- Customer Experience Enhancement: Ensure automated processes improve, not complicate, customer interactions
- Revenue Impact: Focus automation efforts on activities directly influencing business growth and profitability
- Team Development: Design automation systems that allow team members to focus on high-value work requiring creativity and critical thinking
- Scalability Planning: Select automation technologies that accommodate future expansion without extensive reconfiguration
Step 3: Select the Right Tools for Your Automation Needs
The automation services and business process automation tools landscape offers thousands of solutions. Choosing the right tools requires careful evaluation of specific needs, integration capabilities, and scalability.
Essential Business Process Automation Tools by Category
Workflow Automation Platforms
- Zapier: Connects 5,000+ apps for no-code automation workflows
- Microsoft Power Automate: Enterprise-grade automation for Microsoft ecosystems
- Make (formerly Integromat): Advanced automation for complex processes
Robotic Process Automation Solutions
- UiPath: Industry-leading RPA platform for large enterprise automation
- Automation Anywhere: Cloud-native RPA with AI capabilities
- Blue Prism: Enterprise RPA focused on financial services and regulated industries
AI-Powered Automation
- IBM Watson: Advanced artificial intelligence for decision-making and natural language processing
- Google Cloud AI: Machine learning tools for predictive analytics and automation
- Amazon Bedrock: Generative AI services for building custom AI agents
Marketing Automation
- HubSpot: Comprehensive inbound marketing and sales automation
- Marketo: Enterprise marketing automation for complex campaigns
- ActiveCampaign: Email automation and customer relationship management for small business
Customer Support Automation
- Zendesk: Complete customer support platform with AI-powered automation
- Intercom: Conversational relationship platform with intelligent chatbots
- Freshdesk: Affordable customer support automation for businesses of all sizes
Financial Automation
- QuickBooks: Accounting automation for small business and growing companies
- SAP Concur: Expense management and accounts payable automation
- Bill.com: Automated payment processing and accounts payable workflows
Evaluation Criteria for Automation Software
When selecting business automation software, assess:
Integration Capabilities: Seamless connection with existing systems prevents data silos and ensures end-to-end automation
Scalability: Solutions should accommodate growing business operations without platform migration
User Experience: Intuitive interfaces minimize training requirements for team members
Security Standards: Particularly critical for sensitive data and compliance in financial services
Vendor Support: Reliable technical support and comprehensive documentation accelerate automation implementation
Total Cost of Ownership: Consider licensing, implementation, training, and maintenance costs beyond initial investment
Step 4: Implement and Test Your Automation Strategy
Successful automation implementation follows a phased approach that minimizes disruption while maximizing learning opportunities.
The Pilot Program Approach
Start Small: Begin with a single business process that represents a contained automation opportunity
- Select a process with clear metrics for success measurement
- Choose an area where failure won’t critically impact business operations
- Ensure the pilot demonstrates automation value to stakeholders
Build Cross-Functional Teams: Successful automation requires collaboration:
- Process owners who understand current workflows
- IT professionals managing technical implementation
- End users who will work with automated systems
- Business leaders providing strategic direction
Establish Testing Protocols: Rigorous testing prevents costly errors:
- Validate automated workflows against multiple scenarios
- Test edge cases and exception handling
- Verify data accuracy and system integration
- Confirm user experience meets expectations
Managing Change and Training
Employee Communication: Address concerns about automation displacing jobs by emphasizing how automation systems augment human capabilities rather than replace team members
Comprehensive Training: Develop training programs covering:
- How automated processes work
- When human intervention is required
- Troubleshooting common issues
- Optimizing workflow efficiency
Feedback Mechanisms: Create channels for users to report issues and suggest improvements to automation workflows
Case Study: Small Business Automation Success
A boutique e-commerce retailer implemented marketing automation and inventory management systems:
Initial State:
- 40 hours monthly spent on manual email marketing
- Frequent stockouts due to manual inventory tracking
- Customer satisfaction score of 3.2/5
Automation Implementation:
- Klaviyo for email automation and customer segmentation
- TradeGecko for automated inventory management
- Zendesk chatbots for basic customer support
Results After 6 Months:
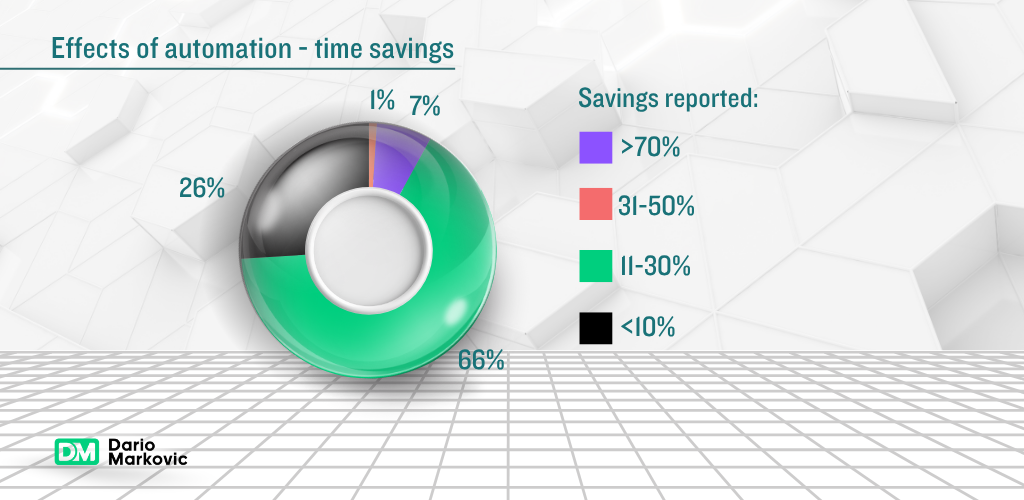
- Marketing time reduced to 8 hours monthly (80% reduction)
- Stockouts decreased by 92%
- Customer satisfaction improved to 4.6/5
- Revenue increased 34% with same team size
Step 5: Monitor, Optimize, and Scale Your Automation Systems
Automation implementation is not a one-time project but an ongoing automation journey requiring continuous process improvement.
Performance Monitoring Framework
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
Track metrics that matter:
- Process Efficiency: Time-consuming process saved, throughput increased, bottlenecks eliminated
- Cost Metrics: Labor costs reduced, operational costs decreased, ROI achieved
- Quality Measures: Error rates, accuracy improvements, compliance maintained
- Customer Impact: Customer satisfaction scores, response times, resolution rates
- Employee Metrics: Time freed for strategic work, job satisfaction, adoption rates
Real-Time Dashboards: Implement monitoring tools that provide visibility into:
- Automation workflow performance
- Exception rates requiring human intervention
- System uptime and reliability
- Integration health across business functions
Continuous Optimization Strategies
Regular Reviews: Schedule quarterly automation audits to:
- Identify underperforming automated processes
- Discover new automation opportunities
- Assess emerging automation technologies
- Gather user feedback on automated systems
A/B Testing: Continuously test variations in automated workflows to optimize:
- Email automation subject lines and content
- Customer support chatbot responses
- Sales automation outreach sequences
- Inventory management reorder triggers
Process Mining: Use advanced analytics to discover inefficiencies invisible to manual analysis. MIT Sloan research demonstrates that process mining identifies optimization opportunities missed in 67% of traditional audits.
Scaling Automation Across the Organization
Once pilot programs prove successful, expand automation systematically:
Horizontal Scaling: Replicate successful automation to similar processes across departments
Vertical Integration: Connect automated processes for end-to-end automation spanning multiple business functions
Advanced Capabilities: Layer AI-powered automation onto existing automation workflows for intelligent decision-making
Enterprise Automation: Transition from point solutions to comprehensive business process automation software platforms
Best Practices for Business Automation Success
Strategic Considerations
- Start with Business Needs, Not Technology: The right tools emerge from clearly defined specific needs rather than chasing trending automation technologies
- Maintain Human-Centered Design: Even fully automated systems should enhance user experience for both employees and customers
- Balance Automation and Human Touch: Some business tasks benefit from personal attention. Know when automation improves versus diminishes customer experience
- Plan for Exceptions: Robust automated systems include clear escalation paths for scenarios requiring human intervention
Technical Best Practices
Document Everything: Create comprehensive documentation for:
- Automation workflows and logic
- Integration points and dependencies
- Troubleshooting procedures
- Maintenance requirements
Implement Version Control: Track changes to automation rules and configurations to enable rollback when necessary
Build Redundancy: Design automation systems with backup processes preventing complete failure
Prioritize Security: Protect sensitive data through encryption, access controls, and regular security audits
Organizational Best Practices
Executive Sponsorship: Secure commitment from business leaders to ensure resources and organizational support
Change Management: Address cultural resistance through transparent communication about automation benefits
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Break down silos by involving stakeholders from all affected business operations
Celebrate Wins: Recognize teams and individuals contributing to successful automation implementation
Overcoming Common Automation Challenges
Technical Hurdles
Legacy System Integration: Many organizations struggle connecting modern automation tools with outdated systems
- Solution: Use API-based integration platforms or RPA to bridge technology gaps
Data Quality Issues: Automation amplifies problems with inconsistent or inaccurate data
- Solution: Implement data governance and cleansing processes before automation
Complexity Management: Complex processes may resist straightforward automation
- Solution: Decompose into smaller, manageable components for incremental automation
Organizational Obstacles
Employee Resistance: Fear of job displacement creates friction during automation implementation
- Solution: Emphasize augmentation over replacement, retrain affected team members for higher-value roles
Budget Constraints: Automation requires upfront investment that may challenge small business budgets
- Solution: Start with affordable tools, demonstrate ROI through pilots, then scale investment
Skills Gaps: Organizations may lack expertise for advanced automation technologies
- Solution: Partner with automation services providers, invest in training, hire specialists for complex implementations
Strategic Pitfalls
Automating Broken Processes: Automation makes bad processes faster, not better
- Solution: Optimize workflows through process improvement before automation
Over-Automation: Attempting too much automation too quickly overwhelms organizations
- Solution: Follow phased implementation prioritizing high-impact automation opportunities
Neglecting Maintenance: Automated systems require ongoing attention to remain effective
- Solution: Allocate resources for monitoring, optimization, and updates throughout the automation journey
The Future of Business Automation: Emerging Trends
Generative AI and Intelligent Automation
The convergence of artificial intelligence and automation is creating unprecedented capabilities. According to PwC, AI could contribute $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030, with automation playing a central role.
AI Agents: Autonomous systems that understand context, make decisions, and execute complex tasks across multiple business functions without human intervention
Conversational AI: Natural language processing enabling sophisticated interactions between humans and automated systems
Predictive Automation: Systems that anticipate needs and proactively execute actions before problems occur
Hyperautomation
This approach combines multiple automation technologies: RPA, AI, process mining, and analytics, to create comprehensive automation ecosystems that maximize operational efficiency.
Low-Code/No-Code Platforms
Democratizing automation through visual development environments that enable business users without technical backgrounds to create automated workflows and custom automation solutions.
Industry-Specific Automation
Specialized automation solutions addressing unique needs in:
- Financial Services: Regulatory compliance, fraud detection, and risk assessment automation
- Healthcare: Patient scheduling, claims processing, and clinical decision support
- Manufacturing: Supply chain management, quality control, and predictive maintenance
- Retail: Inventory management, personalization, and omnichannel customer experience
Getting Started: Your 90-Day Business Automation Roadmap
Days 1-30: Assessment and Planning
Week 1-2: Conduct comprehensive process audit identifying automation opportunities
Week 3: Prioritize processes using impact/effort matrix
Week 4: Define success metrics and select pilot process
Days 31-60: Tool Selection and Implementation
Week 5: Research and evaluate business process automation tools
Week 6: Select solution and develop implementation plan
Week 7-8: Configure automation, test thoroughly, and train users
Days 61-90: Launch and Optimization
Week 9: Launch pilot program with close monitoring
Week 10-11: Gather feedback, optimize workflows, address issues
Week 12: Evaluate results, document learnings, plan expansion
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Automation for Business Growth
Implementing an effective business automation guide strategy transforms how organizations operate, compete, and grow. The businesses that thrive in 2026 and beyond will be those that strategically deploy automation technologies to eliminate time-consuming tasks, enhance customer experience, and empower team members to focus on work requiring uniquely human capabilities like creativity, empathy, and critical thinking.
The key to successful automation lies not in the technology itself, but in the thoughtful application of the right tools to address specific business needs. By following this step-by-step guide, identifying opportunities, setting clear objectives, selecting appropriate solutions, implementing carefully, and continuously optimizing, organizations of all sizes can harness the cost savings, operational efficiency, and competitive advantages that business automation delivers.
Start your automation journey today. Begin small, learn quickly, and scale systematically. The investment you make in business automation now will compound over time, creating sustainable advantages that position your organization for long-term success in an increasingly automated world.
Remember, the goal isn’t to replace human workers but to augment their capabilities, allowing your team to focus on strategic initiatives that drive true business value and differentiation in the marketplace.
FAQs About Business Automation
What is the difference between RPA and AI-powered automation?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) uses software robots to execute rule-based, repetitive tasks by mimicking human actions. AI-powered automation leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to handle complex processes requiring decision-making, pattern recognition, and continuous learning.
RPA works best for structured, predictable workflows, while AI automation handles unstructured data and adapts to changing conditions.
How much does business automation typically cost?
Business automation costs vary widely based on scope and complexity. Small business automation using tools like Zapier or HubSpot starts at $20-200 monthly. Mid-market solutions for comprehensive workflow automation range from $5,000-50,000 annually.
Enterprise robotic process automation platforms can require $100,000+ investments plus implementation costs. However, most organizations achieve positive ROI within 6-18 months through labor cost reduction and operational efficiency gains.
Will automation replace my employees?
Business automation is designed to augment human capabilities, not replace team members. While automation handles repetitive tasks and manual processes, it frees employees to focus on strategic work requiring critical thinking, creativity, and interpersonal skills.
Organizations typically redeploy staff to higher-value activities rather than reducing headcount. The most successful automation implementations upskill existing team members to work alongside automated systems.
What processes should I automate first?
Start with high-impact, low-complexity processes that deliver quick wins and build organizational confidence. Ideal initial automation opportunities include: email automation and marketing activities, basic customer support responses, data entry and document management, employee onboarding workflows, and invoice processing or accounts payable.
These prove automation value before tackling more complex processes like supply chain management or advanced AI applications.
How do I measure the success of my automation initiatives?
Track both quantitative and qualitative metrics including: time savings (hours reclaimed from manual processes), cost reduction (decreased labor costs and operational expenses), error rates (reduction in human error), customer satisfaction scores, employee productivity and satisfaction, process completion time, and overall ROI comparing automation investment against realized benefits.
Establish baseline measurements before implementation to accurately quantify improvement from automated systems.