The ecommerce business industry is booming, with businesses of all sizes leveraging different ecommerce business models to maximize their success.
Whether you’re a startup or an established brand, choosing the right e-commerce model can make all the difference.
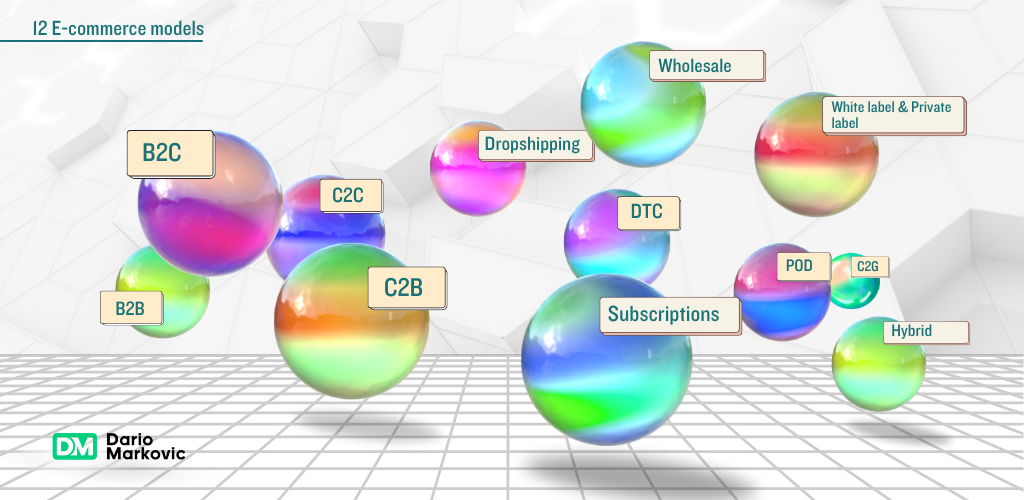
In this guide, we explore together twelve powerful e commerce models for your ecommerce business that can take your to the next level.
Understanding E-Commerce Business Models
What is an E-Commerce Business Model?
The ecommerce market is one of the fastest-growing industries worldwide, with global e-commerce sales expected to reach \$7.4 trillion by 2025. In Southeast Asia alone, the market is expanding rapidly, with Indonesia projected to generate $150 billion in online retail sales by 2030, making up over 40% of the region’s market.
This growth is fueled by increased internet access, mobile commerce, and a rising middle class. Other emerging markets, including Malaysia, the Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam, are also seeing a surge in e-commerce adoption.
As online shopping evolves, businesses must adopt the right ecommerce business model to stay competitive and maximize profitability. An e-commerce business model defines how a company operates, delivers value, and sells products or services online.
There are several types of ecommerce business, each catering to different audiences and offering unique advantages.
Common e-commerce business models include:
-
Business-to-Business (B2B) – Companies sell products or services to other businesses.
-
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) – Businesses sell directly to end consumers.
-
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) – Individuals sell goods or services to other individuals.
-
Consumer-to-Business (C2B) – Individuals offer products or services to businesses.
-
Business-to-Government (B2G) – Businesses provide products or services to government agencies.
-
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) – Brands sell directly to consumers without intermediaries.
-
Hybrid Models – Companies integrate multiple ecommerce models approaches to maximize reach and profitability.
Building a Strong Ecommerce Model Foundation
Once you select an ecommerce model, focus on:
-
Developing a Business Plan – Outline your strategy for product sourcing, marketing, and logistics.
-
Choosing a Delivery Framework – Assess which fulfillment strategy best suits your business, whether it’s dropshipping, warehousing, or print-on-demand.
-
Optimizing Customer Experience Surveys – Invest in seamless website navigation, efficient payment processing, and personalized marketing strategies.
E-commerce is a dynamic and ever-evolving space, and choosing the right e business model sets the foundation for long-term success.
Top 12 Types of Ecommerce Business Models to Look at in 2025
When I first ventured into the world of ecommerce business, I had no idea what I was doing. I knew I wanted to sell products online and generate extra income, but I quickly discovered that the landscape was far more complex than I had imagined. With so many different ecommerce business models available, each with its own set of advantages and challenges, it took time to find the right fit.
Through trial and error, I experimented with multiple ecommerce models. Some proved to be highly successful, while others turned out to be complete failures. However, these experiences provided invaluable lessons on what makes an ecommerce business thrive.
I’ll walk you through 12 of the most popular ecommerce business models you can use to start and scale your online business in 2025.
From the well-known B2B and B2C models to innovative approaches like subscription services and hybrid marketplaces, this guide will help you understand the best options available.
Whether you’re launching your first store or considering a pivot to a new business model, this breakdown will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Let’s dive in!
1. Business-to-Consumer (B2C)

The Business-to-Consumer (B2C) model is the most common ecommerce framework, where businesses sell goods or services directly to individual consumers. Transactions occur through online marketplaces, company websites, or social media platforms.
Companies like Amazon, Walmart, and Shopify-based stores exemplify this model.
How It Works:
-
Businesses list products on an online platform.
-
Consumers browse and make purchases directly through digital storefronts.
-
Payment processing, order fulfillment, and customer service are handled online.
-
Marketing strategies like SEO, social media, and email campaigns are used to drive traffic.
Advantages:
-
Large and diverse customer base
-
Simplified marketing strategies through direct consumer targeting
-
High scalability potential with automation and digital marketing tools
Challenges:
-
Intense competition with many brands vying for consumer attention
-
Necessity for strong branding and customer loyalty to retain customers
2. Business-to-Business (B2B)

The Business-to-Business (B2B) e-commerce model involves transactions between businesses rather than direct sales to consumers. Companies that operate under this model provide products, services, or software solutions tailored to other businesses, helping them streamline operations, reduce costs, or enhance efficiency.
Common B2B businesses include wholesalers, manufacturers, and service providers such as Alibaba, Salesforce, and Shopify Plus.
How It Works:
-
Businesses typically purchase products or services in bulk, resulting in higher revenue per sale.
-
Transactions often involve negotiations, contracts, and customized pricing based on order volume.
-
Companies establish long-term relationships, as procurement decisions involve multiple stakeholders.
-
Digital platforms like B2B marketplaces, SaaS providers, and supplier networks facilitate transactions.
Advantages:
-
Higher Order Value: Since businesses buy in bulk, transactions yield more revenue per sale compared to B2C.
-
Predictable Revenue: Long-term contracts and repeat purchases ensure stable cash flow.
-
Stronger Customer Relationships: Building partnerships leads to long-term loyalty and trust.
Challenges:
-
Complex Sales Cycle: Unlike B2C, B2B transactions involve multiple decision-makers, requiring strategic sales efforts.
-
Extended Payment Terms: Businesses may negotiate delayed payments, impacting cash flow.
-
High Customer Acquisition Costs: Attracting and converting B2B clients often requires dedicated sales teams and marketing investments.
3. Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)

Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) ecommerce business model enables individuals to buy and sell products directly to one another via online platforms.
This ecommerce model is commonly seen on sites like eBay, Craigslist, and Facebook Marketplace.
How It Works:
-
Sellers list products on a marketplace platform.
-
Buyers browse, make purchases, and arrange transactions.
-
Platforms facilitate secure payments and dispute resolution.
-
Revenue is generated through listing fees, transaction fees, and automate social media marketing.
Advantages:
-
Low operational costs for sellers with minimal infrastructure requirements.
-
Revenue potential through commissions and fees for marketplace platforms.
-
Direct peer-to-peer transactions enable personalized sales experiences.
Challenges:
-
Regulation difficulties with verifying seller credibility and product quality.
-
Higher risk of fraud and disputes due to unregulated transactions.
-
Limited scalability for individual sellers.
4. Consumer-to-Business (C2B)
In the Consumer-to-Business (C2B) model, individuals sell goods, services, or digital assets to businesses.
This approach is common among freelancers, influencers, and content creators using platforms like Upwork, Fiverr, and social media partnerships.
How It Works:
-
Consumers create and offer services (e.g., graphic design, consulting, sponsored content).
-
Businesses browse listings or directly approach individuals for services.
-
Transactions are completed through bidding, fixed pricing, or contractual agreements.
-
Revenue is generated through service fees, commissions, or advertising partnerships.
Advantages:
-
Flexible pricing models allow consumers to set their own rates.
-
Businesses gain niche expertise through specialized freelancers or influencers.
-
Lower overhead costs for businesses compared to hiring full-time employees.
Challenges:
-
High competition makes it difficult for individuals to stand out.
-
Reliance on reputation and ratings to secure projects.
-
Payment security concerns due to delayed or disputed transactions.
5. Dropshipping Ecommerce Model
Dropshipping is an ecommerce business model that allows retailers to sell products without holding inventory. Instead, when a retailer receives an order, they purchase the item from a third-party supplier, who then ships it directly to the customer.
This model eliminates the need for warehousing and upfront investment in stock, making it an attractive option for new entrepreneurs and online sellers looking to minimize risk.
How It Works:
-
The retailer lists products on an online store without physically stocking them.
-
When a customer places an order, the retailer purchases the product from a supplier.
-
The supplier ships the product directly to the customer on behalf of the retailer.
-
The retailer profits from the difference between the selling price and the supplier’s price.
Advantages:
-
Low Upfront Investment: No need for inventory storage or large capital outlay.
-
Wide Product Variety: Access to an extensive range of products without risk.
-
Flexibility: Operate from anywhere with an internet connection.
Challenges:
-
Lower Profit Margins: Due to competition and supplier costs.
-
Dependence on Third-Party Suppliers: Delays and quality control issues can arise.
-
Limited Branding Opportunities: Retailers don’t control packaging or fulfillment.
6. Direct-to-Consumer (DTC)
The Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) ecommerce model allows brands to bypass traditional retailers and wholesalers, selling directly to consumers. This approach gives businesses greater control over branding, pricing, and customer experience, often leading to higher profit margins and stronger customer relationship
Examples include Warby Parker and Glossier.
How It Works:
-
Companies manufacture or source their own products.
-
They sales process goes directly through their websites, social media, or proprietary platforms.
-
Brands manage fulfillment, customer service, and marketing in-house.
Advantages:
-
Higher Profit Margins: No middlemen, allowing for greater revenue retention.
-
Greater Brand Control: Direct interaction with customers enhances loyalty and trust.
-
Data-Driven Decision Making: Full access to customer data for optimized marketing and product development.
Challenges:
-
Customer Acquisition Costs: Brands must invest heavily in digital marketing and paid advertising.
-
Logistics and Fulfillment Management: Requires efficient supply chain coordination.
-
Increased Competition: Competing with established retailers can be challenging.
7. Subscription Business Model

The subscription-based ecommerce model provides customers with products or services on a recurring basis, ensuring predictable revenue for businesses. This model has gained significant traction across various industries, from entertainment and beauty to food and software.
Popular examples include Netflix, Dollar Shave Club, and HelloFresh.
How It Works:
-
Customers subscribe to a recurring service (monthly, quarterly, or annually).
-
Businesses deliver products or services based on the subscription plan.
-
Companies focus on retaining customers through personalized experiences and consistent value delivery.
Advantages:
-
Consistent Revenue Streams: Predictable income through recurring billing.
-
High Customer Retention Rates: Builds long-term relationships with consumers.
-
Scalability: Subscription models can expand product offerings over time.
Challenges:
-
Customer Churn: Retaining subscribers requires continuous engagement and value.
-
High Initial Customer Acquisition Costs: Businesses must invest in marketing and incentives to attract new subscribers.
-
Product or Service Fatigue: Customers may lose interest over time, necessitating constant innovation.
8. Wholesale
The wholesale ecommerce model involves businesses purchasing bulk products at reduced costs and reselling them at a markup. This model is commonly used by retailers, distributors, and manufacturers looking to supply goods to other businesses.
Examples include Costco and DHGate.
How It Works:
-
Manufacturers or distributors sell large quantities of products to retailers or businesses.
-
Buyers resell the products to consumers or other businesses at a profit.
-
Transactions often involve negotiated pricing and long-term contracts.
Advantages:
-
High Revenue Potential: Large order volumes generate substantial profits.
-
Stable and Scalable: Long-term contracts provide business stability.
-
Efficient Supply Chain: Bulk purchasing reduces per-unit costs.
Challenges:
-
Significant Capital Investment: Requires upfront purchasing of large stock volumes.
-
Complex Inventory Management: Handling bulk goods necessitates advanced logistics.
-
Dependency on B2B Clients: Revenue relies on maintaining relationships with buyers.
9. White Label & Private Label

The White Label and Private Label ecommerce models allow businesses to sell trending products on Shopify manufactured by third parties under their own brand.
White labeling involves selling generic products with custom branding, while private labeling allows businesses to develop unique formulations or packaging.
Amazon FBA sellers often utilize this model.
How It Works:
-
Companies partner with manufacturers to produce goods.
-
Products are branded and marketed under the retailer’s name.
-
Businesses control pricing, marketing, and sales strategies.
Advantages:
-
Full Brand Control: Businesses can create a unique brand identity.
-
Increased Profit Margins: Direct branding eliminates competition on the same product.
-
Low Manufacturing Overhead: No need for in-house production.
Challenges:
-
Requires Manufacturer Partnerships: Finding reliable suppliers is crucial.
-
High Initial Investment Costs: Branding and packaging design add upfront costs.

10. Print-on-Demand (POD)
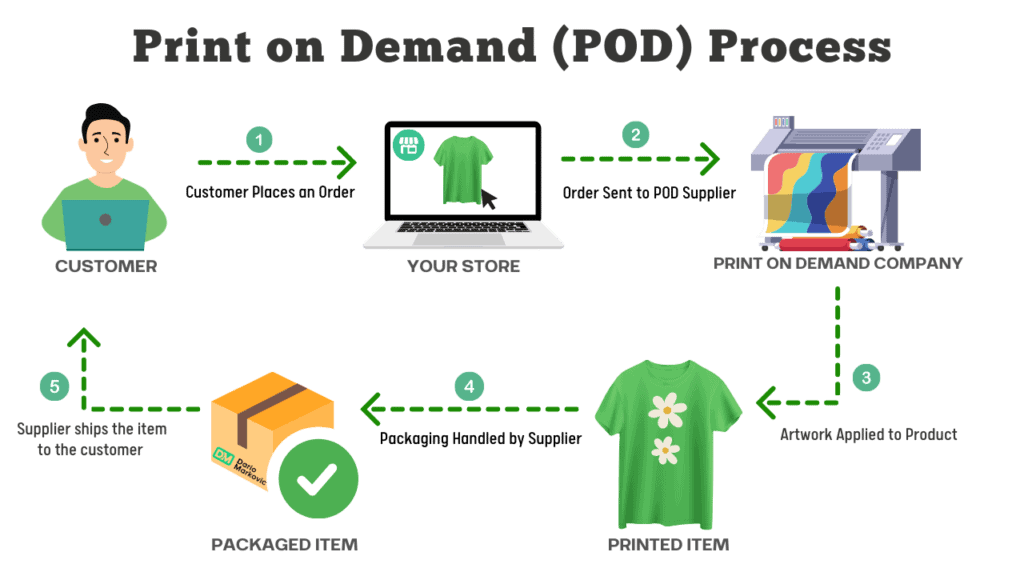
Print-on-demand businesses create and sell custom-designed products that are produced only after an order is placed. This eliminates the need for inventory storage and minimizes upfront costs, making it an attractive model for designers and entrepreneurs.
Platforms like Printful and Teespring are key players.
How It Works:
-
Businesses create unique designs and list them on online storefronts.
-
When a customer orders, the product is printed and shipped by a third-party provider.
-
The retailer profits from the markup on each sale.
Advantages:
-
No Inventory Management: Products are only made when purchased.
-
Unlimited Creative Potential: Customization options attract niche audiences.
-
Low Financial Risk: No need to pre-purchase bulk stock.
Challenges:
-
Lower Profit Margins: Production costs per item are higher than bulk manufacturing.
-
Dependence on External Suppliers: Production speed and quality control rely on third parties.
-
Limited Product Range: Some products may not be available for print-on-demand services.
11. Hybrid
The Hybrid ecommerce model blends multiple strategies, such as combining B2B and DTC approaches or integrating online and offline sales.
This flexible approach allows businesses to maximize reach and revenue by catering to different customer segments.
Amazon exemplifies this approach by integrating B2C retail with B2B services.
How It Works:
-
Businesses implement multiple connective ecommerce strategies simultaneously.
-
They may sell directly to consumers while also supplying bulk products to retailers.
-
Brands leverage diverse marketing and fulfillment methods to optimize sales.
Advantages:
-
Diversified Revenue Streams: Reduces reliance on a single business model.
-
Greater Audience Reach: Serves both direct consumers and business clients.
-
Increased Resilience: Adaptable to market changes and economic shifts.
Challenges:
-
Complex Logistics and Marketing: Requires efficient coordination of multiple operations.
-
Higher Operational Costs: Managing different sales channels can be resource-intensive.
-
Brand Positioning Challenges: Maintaining a consistent brand message across models.
12. Consumer-to-Government (C2G)
The Consumer-to-Government (C2G) ecommerce model involves transactions between individuals and government agencies.
This model is commonly used for tax payments, license renewals, utility bill payments, and other public services.
How It Works:
-
Consumers access government portals or third-party platforms to complete transactions.
-
Payments, applications, or requests are processed electronically.
-
Governments utilize digital solutions to streamline administrative services.
Advantages:
-
Convenience: Citizens can access services online without visiting physical offices.
-
Efficiency: Reduces paperwork and processing times.
-
Secure Transactions: Government systems ensure high data security standards.
Challenges:
-
Limited Market Scope: Restricted to specific government services.
-
Bureaucratic Inefficiencies: Slow adoption of digital transformation in some regions.
How to Choose the Right Ecommerce Business Model?
Choosing the right e business model is essential for your online business success. You need a model that aligns with your goals, resources, and target market.
Here are key factors to consider:
a. Research Your Target Market
Understand your ideal target audience, their needs, preferences, and buying habits. Conduct market research to identify opportunities.
For example, a subscription model suits busy professionals, while a marketplace appeals to bargain hunters.
b. Analyze your Skills & Resources
Different or other business models require varying levels of expertise. If you excel in product development, private label or DTC might work.
If marketing is your strength, dropshipping or affiliate marketing could be better suited.
c. Consider Startup Costs
Some models require more upfront investment. Private label and DTC need capital for manufacturing and marketing, while dropshipping and affiliate businesses have lower startup costs.
d. Evaluate Profit Margins
Profitability varies by model. Service-based businesses may have lower margins but high volume potential. DTC offers higher margins due to pricing control. Assess profit potential before deciding.
e. Determine Inventory Management Needs
Finally, consider how much inventory you can handle. DTC and private label require inventory management, while dropshipping eliminates this burden.
Selecting the right e business model depends on your goals, market, and resources. Weigh the pros and cons to make an informed decision and set your business up for success.
Key Elements of a Successful Ecommerce Business Model
Nine key elements make up a successful e commerce business model.
I’ve seen firsthand how critical each one is.
1. Value Proposition
Your value proposition is the heart and soul of your business model. It sets you apart from competitors and convinces customers to buy from you.
I always ask myself: What unique value do we provide? How do we solve customers’ problems better than anyone else? Nailing this is essential for your ecommerce success.
2. Customer Segments
Knowing exactly who your target market is is crucial.
Creating detailed buyer personas based on demographics, interests, and behaviors helps tailor everything from your product offerings to your marketing strategy.
I segment my customers to personalize their experiences and build stronger relationships. It’s a game-changer.
3. Channels
Your sales and marketing channels are how you reach and engage customers. I use a multi-channel approach, including my ecommerc website, online marketplaces, social media, email, and even offline events. Understanding your customers’ preferences and optimizing each channel for maximum impact is key.
Experiment and analyze results to tune your strategy with your ecommerce models.
4. Customer Relationships
Building strong, lasting customer relationships is the foundation of customer retention and loyalty. I prioritize exceptional customer service, personalized communications, and rewarding loyal customers. Regularly seeking feedback and acting on it shows customers you value them.
Engaged, happy customers become your best advocates and drive referrals.
5. Revenue Streams
Your revenue model is how you make money. I diversify my income sources beyond just selling products online. Subscriptions, services, affiliate marketing vs advertising are all great options. Look for opportunities to cross-sell and upsell to maximize revenue from each customer.
Continuously test and optimize your pricing and revenue models.
Read this blog automated business ideas to make more money online.
6. Key Resources
Your key resources are the assets that allow your business ecommerce models to function. This includes physical, intellectual, human, and financial resources.
I invest in top talent, cutting-edge tech, and strong supplier relationships. Protecting intellectual property like brand names and patents is also vital.
7. Key Activities
These are the most important things you do to operate your business model. For me, it’s product development, marketing, order fulfillment, and customer support. I optimize these processes through automation, outsourcing, and continuous improvement.
Efficient, effective operations are a competitive advantage.
8. Key Partnerships
No business can succeed alone. Key partnerships with suppliers, manufacturers, tech providers, and affiliate marketing reviews help you optimize, scale, and grow. I build mutually beneficial, long-term relationships with partners who share my values and vision.
Together, we can achieve far more than we could alone.
9. Cost Structure
Managing costs is just as important as generating revenue. I aggressively cut unnecessary expenses and look for efficiencies at every turn.
Regularly reviewing and adjusting my cost structure keeps me lean, agile, and profitable as I grow.
Leveraging Social Media in Your E-commerce Business Model
Social media has been a total game-changer for my commerce business. It’s one of the most powerful tools in my marketing arsenal for e business models.
Choosing the Right Social Media Platforms
Not all social media platforms are equally effective. Focus on where your target customers are most active—Facebook and Instagram for broad reach, LinkedIn for B2B networking, and TikTok for engaging Gen Z. Prioritize quality over quantity by doubling down on what works best.
Creating engaging content is key to building a social media community success. Share a mix of educational, entertaining, and inspiring posts that highlight your brand personality.
Videos, stories, polls, and live streams drive the most engagement. User-generated content fosters authenticity and community, while a no-hard-sell approach builds trust.
Influencer Partnerships, Advertising, and Measuring ROI
Influencer marketing amplifies reach and credibility. Partner with influencers aligned with your brand values, leveraging sponsored posts, giveaways, and discounts to build genuine relationships. Authenticity is crucial for effective partnerships.
Paid social advertising is essential for scaling sales. Facebook and Instagram ads provide targeted campaigns with retargeting options for personalized outreach. Continuously test and optimize ad performance to maximize return on ad spend (ROAS).
Tracking ROI ensures strategic refinement. Utilize analytics tools to measure reach, engagement, and conversions. UTM parameters help track social traffic and sales, ensuring data-driven decisions for ongoing success. Social media is an ever-evolving tool that requires consistency, creativity, and adaptability.
Key Takeaways
Understand and master these 9 elements for a successful ecommerce business: value proposition, customer segments, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, partnerships, and cost structure.
Social media can amplify your reach strategically with engaging content and influencer collaborations.
Adapting Your Ecommerce Business Model to Changing Market Trends
The world of e-commerce is constantly evolving. What worked yesterday may not work today, and what works today may not work tomorrow. That’s why it’s crucial to stay on top of the latest trends and adapt your e commerce business model accordingly.
As someone in the trenches of online retail for over a decade, I’ve seen firsthand how quickly things can change. From the rise of mobile commerce to the explosion of social media, there’s always something new on the horizon.
So, how do you stay ahead of the curve? Here are a few key strategies I’ve learned along the way:
Staying agile
One of the biggest mistakes I see ecommerce businesses make is getting too comfortable with their current model. They find something that works and stick with it, even as the market shifts around them.
But here’s the thing: what worked yesterday may not work today. That’s why it’s essential to stay agile and willing to pivot when necessary.
I learned this lesson the hard way back in the early days of my online store. We were selling a particular product line well, but a new competitor entered the market with a similar offering at a lower purchase price point. Suddenly, our sales started to drop.
At first, I was resistant to change. We invested so much time and resources into this product line that I didn’t want to admit defeat. However, as the weeks passed and our revenue continued declining, I realized we had to do something different.
So, we pivoted. We started exploring new product categories and experimenting with different marketing strategies. It wasn’t easy, but it was necessary. And in the end, it paid off. We could adapt to the changing market and become stronger on the other side.
Embracing new technologies
Another key to staying ahead of the curve is embracing new technologies. From artificial intelligence to augmented reality, new tools and platforms are always emerging to help you better serve your customers and streamline your operations.
Of course, keeping up with all the latest tech trends can be overwhelming. That’s why it’s important to be strategic about which technologies you invest in.
Start by identifying the areas of your business that could benefit most from new tools or platforms. Maybe it’s your customer service department or your inventory management system. Then, research and look for solutions that align with your needs and goals.
For example, a few years ago, we implemented a chatbot on our ecommerce website to help handle basic customer inquiries. At first, I was skeptical about whether it would be effective. However, we quickly saw the benefits of reduced response times and increased customer satisfaction.
Since then, we’ve continued to explore other ways to leverage AI and automation in our business. This ongoing process has helped us stay competitive in an increasingly crowded market.
Personalization strategies
Personalization has become a buzzword in the e-commerce world for good reason. Today’s consumers expect a tailored experience that meets their unique needs and preferences.
But personalization isn’t just about adding someone’s name to an email subject line. It’s about leveraging data and insights to create a customized experience at every touchpoint.
We’ve done this in our own business through product recommendations. By analyzing customer behavior and purchase history, we can offer relevant product suggestions that are more likely to convert.
We’ve also experimented with personalized content tailored to customer segments, such as blog posts and email newsletters. By speaking directly to customers’ interests and pain points, we’ve built stronger relationships and driven more engagement.
Of course, personalization isn’t a one-size-fits-all strategy. What works for one ecommerce business may not work for another. The key is to start small, test and iterate, and always keep the customer at the center of your efforts.
Omnichannel approach
In today’s digital age, customers expect a seamless experience across all channels—online, in-store, mobile, and social media. They want to be able to browse products on their phones, buy online, and pick up in-store (or have it delivered same-day).
This is where an omnichannel approach comes into play. It means creating a cohesive brand experience that transcends individual channels or touchpoints.
For example, a customer finds one of your products through an Instagram ad. They click through to your mobile site and add the item to their cart but don’t complete the purchase. Later that day, they receive an abandoned cart email reminding them to check out. They decide to swing by your physical retail store to see the product in person and purchase it there.
This is the power of omnichannel commerce. Connecting the dots between channels can create a more seamless and convenient customer experience.
Of course, implementing an omnichannel strategy isn’t easy. It requires a deep understanding of your customer’s behaviors and preferences and a robust technology stack that can support cross-channel integration.
But the payoff can be significant. According to a study by McKinsey, companies with strong omnichannel strategies retain an average of 89% of their customers, compared to just 33% for those with weak strategies.
Sustainable practices
Finally, no discussion of adapting your ecommerce models would be complete without mentioning sustainability. Today’s consumers are increasingly conscious of their purchases’ environmental and social impact and expect brands to align with their values.
This means looking hard at your supply chain, packaging, and logistics to identify opportunities for reducing waste and minimizing your carbon footprint. It also means being transparent about your sustainability efforts and communicating them clearly to your customers.
One brand that has done this well is Patagonia. The outdoor apparel company has long been a leader in sustainable business practices, from using recycled materials in its products to donating a portion of its profits to environmental causes.
But Patagonia doesn’t just talk the talk—they walk the walk. Over the years, they’ve implemented several innovative sustainability initiatives, such as their “Worn Wear” program, which encourages customers to repair and recycle their old gear instead of buying new.
By making sustainability a core of its brand identity, Patagonia has built a loyal following of customers who share its values. In doing so, it has proven that sustainability and profitability can go hand in hand.
Of course, not every ecommerce business can be a Patagonia. But by taking small steps towards more sustainable practices – switching to eco-friendly packaging or partnering with local suppliers – you can make a meaningful difference, appeal to the growing number of conscious consumers, and make a big name for your small business.
The world of ecommerce is always changing, and staying ahead of the curve requires a willingness to adapt and innovate. By staying agile, embracing new technologies, personalizing the customer experience, taking an omnichannel approach, and prioritizing sustainability, you can position your business for long-term success in an increasingly competitive market.
Key Takeaway:
To thrive in ecommerce, stay agile and ready to pivot. Embrace new tech like AI, personalize customer experience management, adopt an omnichannel approach, and prioritize sustainability. This helps you adapt to market changes and keeps your business competitive.
Personal Favorites- E Commerce Models in 2025
As an entrepreneur, I’ve always been drawn to B2C ecommerce business because of its direct connection with consumers. There’s something incredibly fulfilling about creating a brand, marketing it effectively, and seeing firsthand how customers interact with and benefit from your products.
The ability to scale ecommerce business model, test new marketing strategies, and fine-tune user experience makes B2C highly dynamic. It allows for creativity in branding, storytelling, and engagement, which is something I find extremely rewarding.
Another reason why I would choose B2C repeatedly is the power of data-driven decision-making. With tools like analytics, A/B testing, and best customer feedback tools, optimizing every aspect of the business—from pricing to user experience—is possible. Seeing the immediate impact of marketing efforts and customer engagement makes B2C an exciting space to be in.
Why Subscription-Based E-commerce is a Game Changer?
Subscription-based ecommerce business model is another model I love because it ensures predictable revenue and long-term customer relationships. Unlike one-time sales, subscriptions allow you to build a loyal customer data base that consistently engages with your brand. This model provides financial stability and enables a more strategic approach to scaling.
I’m particularly drawn to the aspect of community-building that comes with subscription services. I’ve implemented this ecommerce business model for Eric Javits as the CEO.
Whether it’s curated monthly boxes or exclusive digital memberships, these models create strong emotional connections between brands and customers. When executed well, they offer a seamless customer experience that keeps people coming back.
For anyone looking for stability, compounded growth, and strong brand engagement, subscription-based ecommerce business model is one of the best choices. That’s why I would opt for it over and over again.
FAQ
- B2C (Business-to-Consumer): Companies sell directly to consumers through online platforms.
- B2B (Business-to-Business): Transactions occur between businesses, such as manufacturers and wholesalers or wholesalers and retailers.
- C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer): Consumers sell directly to other consumers using platforms like eBay or Etsy.
- C2B (Consumer-to-Business): Individuals offer products or services to companies, exemplified by stock photo websites and crowdsourcing platforms.
The six e business models typically include:
B2C
B2B
C2C
C2B
DTC (Direct-to-Consumer)
Subscription-based E-commerce
Amazon operates as both a B2C and B2B platform. While it primarily functions as a B2C marketplace, offering products directly to consumers, it also provides a B2B marketplace (Amazon Business) catering to business customers.
It is B2C search engine but it also offers many B2B software solutions.
There are many real-world examples of C2B marketing strategies, including focus groups, social media engagement, customer reviews, blogs, freelance platforms, polls, and surveys.
Celebrities play a significant role in C2B marketing, as they are often paid to promote products through their social media channels.