Delivering an exceptional customer experience (CX) has become a top priority for businesses across industries. Customer experience KPIs are more than just providing good customer service—it’s about ensuring that every interaction a customer has with your brand, from browsing your website to post-purchase support, is seamless, personalized, and positive.
But how do you know if your CX initiatives are truly making an impact? That’s where Customer Experience KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) come in. These metrics help businesses quantify and evaluate the effectiveness of their CX efforts, enabling them to make data-driven decisions that improve customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention.
In this blog, we’ll explore the most important CX KPIs that every business should track to ensure they’re delivering a top-notch customer experience.
Summary: Top Customer Experience KPIs
Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Metrics: Key metrics like Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) and Net Promoter Score (NPS) help measure overall customer satisfaction and loyalty, providing insights into how likely customers are to recommend your brand and their general happiness with your services.
Operational Efficiency Metrics: KPIs such as Average Response Time (ART) and First Contact Resolution (FCR) focus on how quickly and effectively customer support teams resolve issues, which directly impacts customer satisfaction.
Retention and Value Metrics: Customer Churn Rate, Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), and Retention Rate track the long-term value of customer relationships, helping businesses understand the financial impact of their CX efforts and identify opportunities to improve loyalty and reduce churn.
1. Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
CSAT is one of the most widely used KPIs to measure how satisfied customers are with a specific interaction or overall experience with your brand. Typically, customers are asked to rate their satisfaction on a scale (e.g., 1 to 5 or 1 to 10), and the average score is used to determine overall satisfaction levels.
How to Measure CSAT:
– After a customer support interaction, product purchase, or service completion, you can send a simple survey asking, “How satisfied were you with your experience today?”
– The score is calculated by dividing the number of satisfied customers (those who selected the top positive answers) by the total number of responses.
Why It’s Important:
CSAT provides immediate feedback on how well your business is meeting customer expectations at specific touchpoints. This real-time insight allows you to make quick improvements where needed.
Net Promoter Score (NPS) measures customer loyalty by asking one simple question: “How likely are you to recommend our product or service to a friend or colleague?” Customers respond on a scale from 0 to 10, and they are categorized into three groups:
– Promoters (9-10): Loyal customers who are likely to recommend your brand.
– Passives (7-8): Satisfied but not enthusiastic customers.
– Detractors (0-6): Unhappy customers who are unlikely to recommend your brand and may even discourage others.
How to Calculate NPS:
NPS is calculated by subtracting the percentage of Detractors from the percentage of Promoters. The score can range from -100 to 100.
Why It’s Important:
NPS is a strong indicator of customer loyalty and future growth. A high NPS suggests that your customers are satisfied and willing to act as brand advocates, while a low NPS signals that you need to address underlying issues in your customer experience.
3. Customer Effort Score (CES)
Customer Effort Score (CES) measures how easy it is for customers to interact with your business and resolve their issues. In a CES survey, customers are typically asked, “How easy was it to resolve your issue today?” or “How easy was it to complete your purchase?” Responses are usually on a scale from “very easy” to “very difficult.”
How to Measure CES:
– After key interactions, such as a support request or a transaction, ask customers to rate how much effort they had to put in to achieve their goal.
– A lower CES indicates that customers find it easy to interact with your business, while a higher CES may suggest friction points.
Why It’s Important:
A low-effort experience is a key driver of customer loyalty. Studies show that customers are more likely to remain loyal to brands that make it easy for them to resolve their issues. Tracking CES helps you identify processes that may be creating friction and streamline them to improve the overall customer experience.
4. Customer Churn Rate
Customer churn rate represents the percentage of customers who stop doing business with your company over a given period. This KPI is especially important for subscription-based businesses, but it’s also relevant for any company that relies on repeat customers.
How to Calculate Churn Rate:
Divide the number of customers lost during a specific period by the total number of customers at the beginning of that period. Multiply the result by 100 to get a percentage.

Why It’s Important:
A rising churn rate is a red flag that customers are unhappy with your product or service. Reducing churn directly impacts profitability, as retaining existing customers is often more cost-effective than acquiring new ones. By tracking churn, you can identify dissatisfaction early and take steps to improve CX and retain more customers.
5. Average Response Time (ART)
Average Response Time (ART) tracks how long it takes for your customer support team to respond to customer inquiries, whether via email, chat, phone, or social media. Long wait times can frustrate customers and lead to poor satisfaction ratings, so it’s important to monitor this KPI closely.
How to Measure ART:
– Track the time between when a customer submits a request and when they receive their first response from your support team.
– Measure this across different channels to identify areas for improvement.
Why It’s Important:
In an era of instant communication, customers expect prompt responses. Slow response times can result in frustration and, ultimately, a negative customer experience. Monitoring ART ensures that your team is meeting customer expectations and helps you identify any bottlenecks in your support process.
6. First Contact Resolution (FCR)
First Contact Resolution (FCR) measures the percentage of customer issues that are resolved during the first interaction, without the need for follow-up or escalation. This KPI is closely linked to both customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
How to Measure FCR:
– Divide the number of issues resolved on the first contact by the total number of issues handled. Multiply by 100 to get a percentage.
– This can be tracked across all communication channels, from phone support to live chat and email.
Why It’s Important:
Resolving customer issues quickly and efficiently leads to higher customer satisfaction and reduces operational costs. Customers expect their problems to be solved in a single interaction, and a high FCR rate is a key indicator of an effective support team.
7. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) estimates the total revenue a business can expect to generate from a customer over the entire duration of their relationship. CLV is a powerful KPI for understanding the long-term value of your customer relationships and the impact of your CX initiatives on overall profitability.
How to Calculate CLV:
CLV can be calculated using this formula:
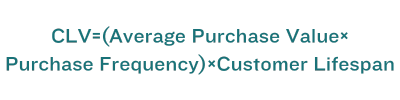
This formula estimates the revenue generated by an average customer over time.
Why It’s Important:
A high CLV indicates that customers are satisfied, loyal, and likely to keep purchasing from your business over time. By improving customer experience, businesses can increase CLV by fostering long-term relationships that drive repeat business and referrals.
8. Retention Rate
Retention rate tracks the percentage of customers who continue doing business with your company over a given period. A high retention rate suggests that customers are satisfied with their experience and are choosing to stay with your brand.
How to Calculate Retention Rate:
Subtract the number of customers lost during a period from the number of customers at the end of the period, divide by the number of customers at the start of the period, and multiply by 100 to get the percentage.

Why It’s Important:
Customer retention is a direct reflection of how well your business is meeting customer needs. A high retention rate is often the result of a strong customer experience strategy, while a low rate can be a sign of underlying issues that need to be addressed.
Wrapping It Up
Tracking the right Customer Experience KPIs is essential for understanding how well your business is delivering on customer expectations. Whether you’re focusing on satisfaction, loyalty, or operational efficiency, these metrics provide valuable insights that can guide your CX strategy and help you make data-driven improvements.
By consistently monitoring and optimizing these KPIs, businesses can foster stronger relationships with their customers, reduce churn, and ultimately drive long-term growth and profitability. Remember, delivering a great customer experience isn’t just about solving problems—it’s about creating positive, memorable interactions that keep customers coming back for more.
FAQ
Customer Experience (CX) KPIs are metrics that help businesses measure the effectiveness of their efforts to deliver positive, seamless, and personalized customer experiences. These KPIs provide insight into customer satisfaction, loyalty, operational performance, and overall engagement with your brand.
CX KPIs are essential because they:
– Quantify customer happiness and loyalty.
– Provide actionable insights for improving customer interactions.
– Help businesses track the success of their CX strategies.
– Identify areas for improvement, such as reducing response times or improving first contact resolution.
Some of the most common CX KPIs include:
– Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): Measures overall customer happiness.
– Net Promoter Score (NPS): Gauges customer loyalty and likelihood to recommend your brand.
– Customer Effort Score (CES): Tracks how easy it is for customers to resolve issues or complete transactions.
– Customer Churn Rate: Monitors the percentage of customers who leave your business over time.
– First Contact Resolution (FCR): Measures how many customer issues are resolved in the first interaction.
CSAT is usually measured by asking customers to rate their satisfaction on a scale (e.g., 1 to 5 or 1 to 10) after a specific interaction or transaction. The overall score is calculated by dividing the number of satisfied customers (usually those who rate you the highest) by the total number of responses and multiplying by 100 to get a percentage
NPS scores range from -100 to 100. Generally:
– Above 0: Indicates more promoters than detractors, which is positive.
– Above 50: Considered excellent, showcasing strong customer loyalty.
– Above 70: World-class, indicating a high likelihood of recommendations from customers.
– NPS measures long-term customer loyalty and how likely customers are to recommend your brand.
– CSAT measures short-term customer satisfaction after specific interactions or transactions.
To reduce churn, focus on:
– Improving customer service by resolving issues quickly.
– Enhancing product or service quality.
– Personalizing customer interactions.
– Listening to customer feedback and addressing pain points.
– Offering loyalty programs to incentivize repeat business.
CES measures how easy it is for customers to resolve an issue or complete a task. It’s important because customers who have to put in less effort are more likely to remain loyal. A lower CES indicates that you’re making interactions as frictionless as possible, enhancing the overall customer experience.
CX KPIs should be tracked continuously or at regular intervals (e.g., monthly, quarterly). For metrics like CSAT and NPS, it’s common to collect feedback immediately after key touchpoints (e.g., customer support interactions, product purchases). Regularly tracking KPIs ensures you can respond quickly to customer issues and optimize your CX strategies.
To improve FCR:
– Provide thorough training to your customer service team.
– Use knowledge bases and AI-driven tools to ensure agents have quick access to relevant information.
– Empower agents to solve problems without escalating the issue.
– Analyze common customer queries and optimize workflows to address these efficiently.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) represents the total revenue you can expect from a customer over the course of their relationship with your business. A strong CX strategy increases CLV by encouraging repeat business, enhancing customer loyalty, and reducing churn. Improving CX can therefore have a direct positive impact on your company’s profitability.
Several tools can help you track and manage CX KPIs, including:
– CRM platforms (e.g., Salesforce, HubSpot) that track customer interactions and feedback.
– Customer feedback platforms (e.g., SurveyMonkey, Qualtrics) for collecting CSAT, NPS, and CES scores.
– Helpdesk software (e.g., Zendesk, Freshdesk) that tracks response times, FCR, and other support metrics.
– Analytics tools (e.g., Google Analytics, Mixpanel) to track customer behavior across digital platforms.
To use CX KPIs effectively:
– Set clear goals for each KPI.
– Regularly monitor and analyze data for trends and insights.
– Identify areas for improvement, such as reducing response times or increasing FCR.
– Implement targeted strategies (e.g., better training, process improvements) based on data insights.
– Continuously test and refine your approach to ensure incremental improvements in CX.
The ideal frequency depends on the customer journey:
– Post-interaction surveys (e.g., after a support call) should be sent immediately to capture real-time feedback.
– Periodic surveys (e.g., quarterly or bi-annually) can be used to measure broader CX metrics like NPS or overall satisfaction.
Be careful not to overwhelm customers with too many surveys, as this can lead to survey fatigue and lower response rates.
By consistently tracking and optimizing CX KPIs, you can:
– Deliver better, more personalized experiences, which can differentiate you from competitors.
– Identify and address customer pain points faster than your competitors.
– Foster higher customer loyalty, reducing churn and driving word-of-mouth referrals.
Ultimately, businesses that prioritize customer experience are better positioned to retain customers and gain a competitive advantage in the market.



